All Clinics Closed 12/24 & 12/25
Holiday Hours
At Aayu Clinics, we redefine healthcare in the heart of Chicago. Our mission is to bring top-notch health services to every individual.
Whether you’re dealing with minor injuries, chronic conditions, or simply seeking preventive care, AAYU is the health clinic nearby that you’ve been searching for. With our dedicated team of board-certified Chicago doctors and physician assistants, we ensure that every patient feels valued and cared for.
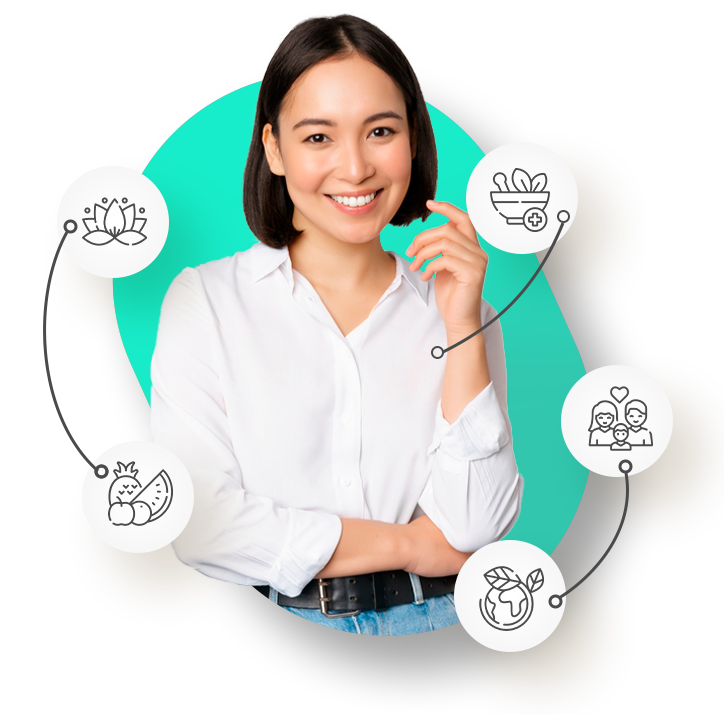

Integrative Medicine for you
and your family.
Balance between food
and well-being
Choices that are good
for the planet
Treatments that are
good for everyone
Medicine that does
not harm health
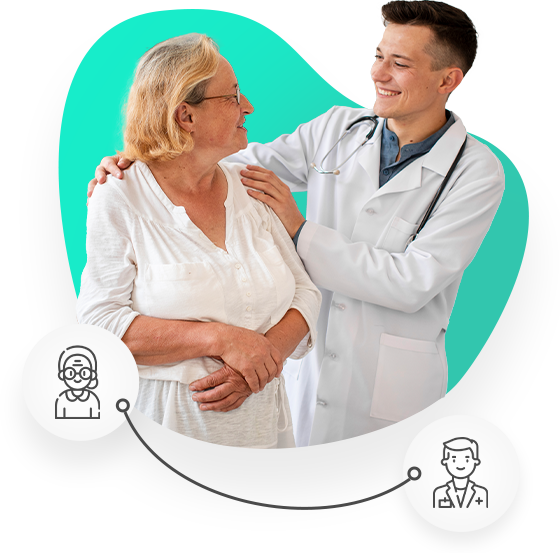
Offering a broad spectrum of health services, AAYU Clinics is more than just a regular health center. From 7-day primary care services to COVID-19 vaccine administration, we’ve got you covered.
Our primary care doctors in Chicago are specialized in handling a range of health concerns, be it blood pressure management or acute sinus infections. If you’re in need of immediate care for minor injuries or have a family medicine doctor on your mind, our health center is equipped to provide timely and efficient care.
We believe that every individual deserves comprehensive and integrated care, and that’s precisely what we deliver.
Navigating the bustling streets of Chicago and looking for a trusted Chicago clinic? Aayu Clinics, with its strategic locations in Lakeview and Wicker Park, ensures you never have to travel far for world-class healthcare.
Find the Aayu Clinic closest to you and schedule an appointment with ease. As a leading Chicago health clinic, we’re focused on ensuring easy access and convenience for all our patients.

No high ER costs, no extra urgent care fees.
Our Primary Care Providers Make All The Difference
Here at Aayu Clinics, we believe in setting the gold standard for healthcare. Our team comprises family nurse practitioners, primary care physicians, and a supporting staff dedicated to ensuring you receive the best care. Every doctor in Chicago IL under our roof is board-certified, ensuring expertise in their respective fields.
With a patient-first approach, we stand out as the clinic Chicago residents trust for their healthcare needs. Whether you’re seeking care for chronic conditions, requiring the services of a physician assistant, or looking for the expertise of a family medicine doctor, Aayu Clinics are equipped and ready to serve.
Remember, when thinking of health care in the Windy City, Aayu is the name to trust. Book an appointment today and experience healthcare like never before.




1. Click on the Book Appointment
2. Pick the clinic or telemedicine
3. In our secure system, choose the service you want
4. Pick the date and time
5. Enter your information
6. The secure, encrypted system will prompt you to take a picture of your ID and insurance card and send it
7. We will verify your insurance and confirm your appointment
Sure, come on in! Also, to avoid a short wait, you can make a same-day appointment.
Please call and let us know! If you lose your appointment slot, there may be a short wait. We will try to address your most pressing problem today.
We work with a wide variety of insurance plans. Please verify we are in-network for you on our insurance page
You can access results in your “patient portal.” If there is anything concerning, we will set up an appointment to review with you.

Lakeview Immediate Care
1645 W School St, Chicago, IL 60657
Wicker Park Immediate Care
1601 W Division St, Chicago, IL 60622
This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience. See our